async函数是使用async关键字声明的函数
async函数是AsyncFunction构造函数的实例, 并且其中允许使用await关键字。async和await关键字让我们可以用一种更简洁的方式写出基于Promise的异步行为,而无需刻意地链式调用promise。
- promise作为返回值
1 | async function func() { |
- 非promise作为返回值
1 | async function func1() { |
上面示例可以得出以下结论:
- 如果async关键字函数显式地返回promise,那就以你返回的promise为准
- 如果async关键字函数返回的不是promise,会自动用Promise.resolve()包装
与promise的对比
先定义一个 Fetch 方法用于获取 github user 的信息
假定:foo1方法依赖于fetchUser,foo2方法依赖于foo1。
1 | function fetchUser() { |
promise方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22// promise
function getUserByPromise() {
fetchUser()
.then((data) => {
//todo soming
console.log(data)
foo1()
.then(res1 => {
// todo soming
console.log(res1)
foo2()
.then(res2 => {
// todo soming
console.log(res2)
})
})
}, (error) => {
console.log(error)
})
}
getUserByPromise()Promise 的方式虽然解决了 callback hell,但是这种方式充满了 Promise的 then() 方法,如果处理流程复杂的话,整段代码将充满 then。语义化不明显,代码流程不能很好的表示执行流程。
async方式
1 | // async |
async 函数完美的解决了上面方式的问题。流程清晰,直观、语义明显。操作异步流程就如同操作同步流程。
async 函数的错误处理
async定义的函数内部会默认返回一个promise对象,如果函数内部抛出异常或者是返回reject,都会使函数的promise状态为失败reject。无法实现预期的效果。故而需要处理相应的错误。
使async函数判定失败reject的场景
内部含有含有直接使用并且未声明的变量或者函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16async function errorFun1 () {
const foo1Result = await foo3()
console.log(foo1Result)
// console.log(foo10())
return a
}
errorFun1()
.then(res => {
console.log('success:', res)
})
.catch(err => {
console.log('fail:', err)
// fail: ReferenceError: a is not defined
// at errorFun1 (index.js:63)
})内部抛出一个错误throw new Error或者返回reject状态return Promise.reject(‘执行失败’)
1 | async function PromiseError() { |
- 函数方法执行出错(Object使用push())
1 | async function errorFun2 () { |
…等等
处理方案
可以用try/catch,遇到函数的时候,可以将错误抛出,并且继续往下执行。
改造一下上面的错误,使其得到预期的结果
1 | async function errorFun1 () { |
测试一下
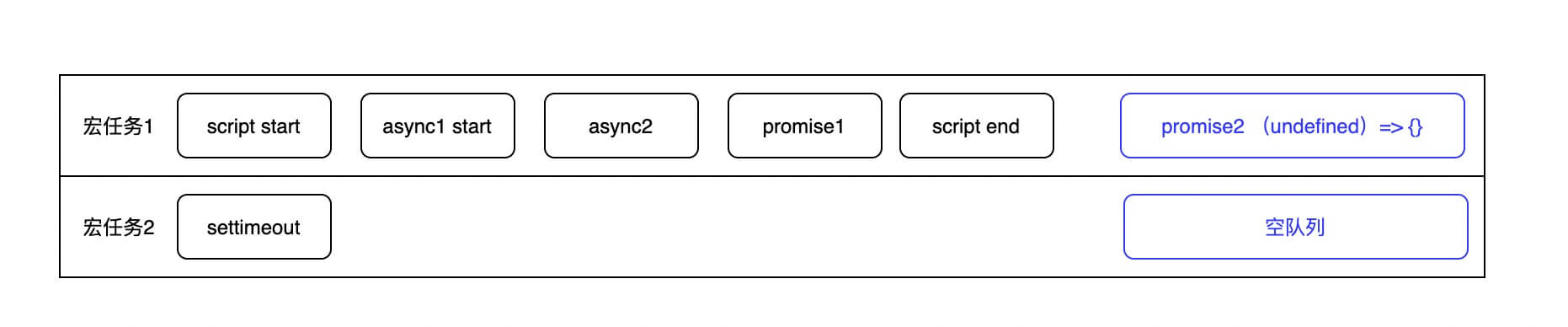
1 | async function async1() { |
事件执行顺序:
执行结果:
1 | script start |